Curative Control
Plants in pest control
1.
Red cedar
2. Milkweed (
Sonchus oleraceus)
Put juice from Milkweed plant on the soil around infested plants to repel wireworm. Milkweed which is also good for melon fly control (Villani; Gould, 1985).
Physical methods
Soil baits
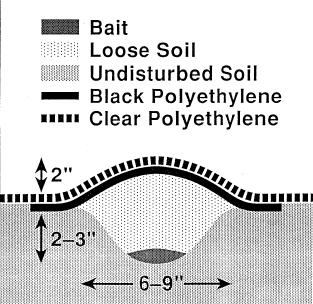
Source: M. Rice
1. Corn/wheat seed mixture bait (Rice, 1999).
Procedure:
Soak mixture in water for 24 hours to facilitate germination.
Place 1/2 cup
(of a 1:1 corn/wheat seed mixture) in a hole that is 12 cm wide and 30 cm deep.
Cover with soil.
Cover the topsoil with plastic to warm the surface and to speed up germination.
Cover the edges with soil to prevent wind from blowing away the plastic.
Remove the plastic, the soil cover, and the bait.
Destroy larvae trapped in the baits.
This method is also used to monitor white grub population.
2. Potato/carrot bait (Ellis; Bradley, 1996: p. 435)
Procedure:
Cut potatoes or carrots into chunks.
Remove the potato 'eyes' to prevent from further growing.
Make the pieces big enough and put in sticks.
Bury "staked potatoes/carrots" at a depth of 3-6 cm in the ground. The stick serves as the handle to easily pull the baits out.
Bury randomly in the field.
Leave baits in the soil for 2-3
days. Wireworm will feed on the baits.
Dispose the baits and the wireworm properly.

